Comparison of Different Extraction Processes on the Physicochemical Properties, Nutritional Components and Antioxidant Ability of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge Kernel Oil
不同工艺提取文冠果仁油理化性质、营养成分及抗氧化能力的比较
Abstract:
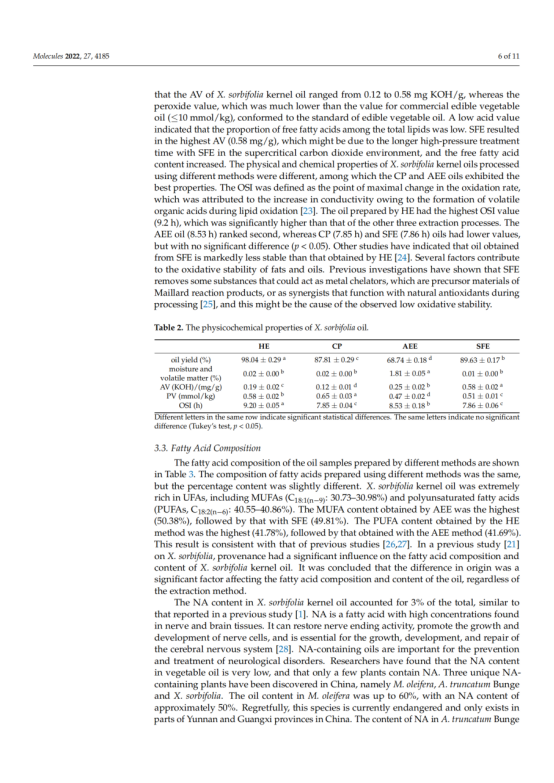
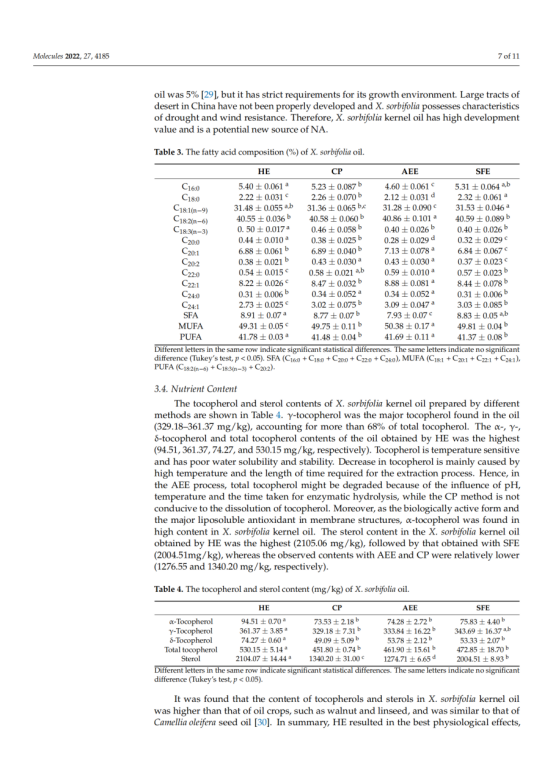
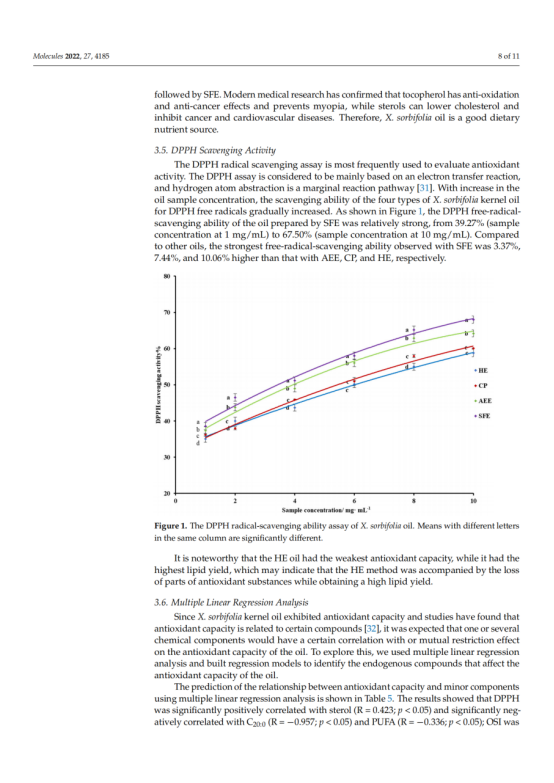
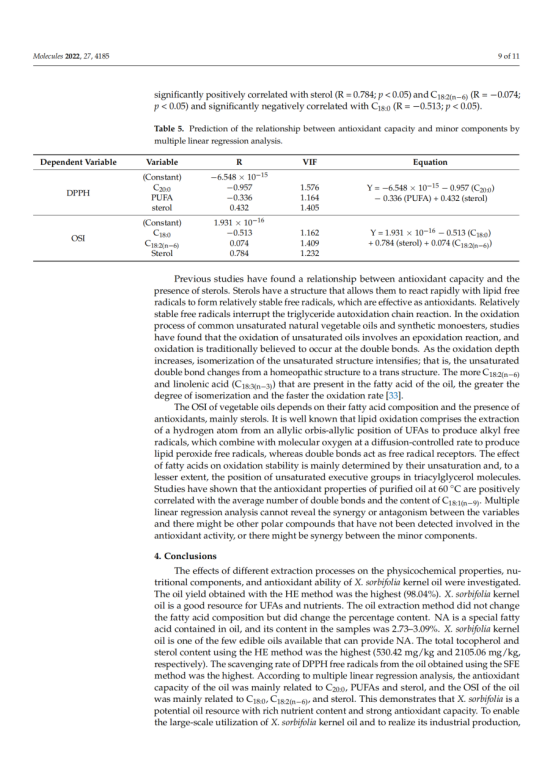
In this study, we investigated and compared the oil yield, physicochemical properties, fatty acid composition, nutrient content, and antioxidant ability of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge (X. sorbifolia) kernel oils obtained by cold-pressing (CP), hexane extraction (HE), aqueous enzymatic extraction (AEE), and supercritical fluid extraction (SFE). The results indicated that X. sorbifolia oil contained a high percentage of monounsaturated fatty acids (49.31–50.38%), especially oleic acid (30.73–30.98%) and nervonic acid (2.73–3.09%) and that the extraction methods had little effect on the composition and content of fatty acids. X. sorbifolia oil is an excellent source of nervonic acid. Additionally, the HE method resulted in the highest oil yield (98.04%), oxidation stability index (9.20 h), tocopherol content (530.15 mg/kg) and sterol content (2104.07 mg/kg). The DPPH scavenging activity rates of the oil produced by SFE was the highest. Considering the health and nutritional value of oils, HE is a promising method for X. sorbifolia oil processing. According to multiple linear regression analysis, the antioxidant capacity of the oil was negatively correlated with sterol and stearic acid content and positively correlated with linoleic acid, arachidic acid and polyunsaturated fatty acid content. This information is important for improving the nutritional value and industrial production of X. sorbifolia.
中文摘要:
本文对冷榨法(CP)、正己烷萃取(HE)、水酶法(AEE)和超临界流体萃取法(SFE)制备的文冠果仁油的出油率、理化性质、脂肪酸组成、营养成分及抗氧化能力进行了研究和比较。结果表明,文冠果油中单不饱和脂肪酸的含量较高(49.31 ~ 50.38%),其中油酸(30.73 ~ 30.98%)和神经酸(2.73 ~ 3.09%)含量最高,提取方法对脂肪酸的组成和含量影响不大。文冠果油是神经酸的极佳来源。此外,HE法的油得率最高(98.04%),氧化稳定指数最高(9.20 h),生育酚含量最高(530.15 mg/kg),甾醇含量最高(2104.07 mg/kg)。SFE产油对DPPH的清除率最高。考虑到油脂的健康和营养价值,HE是一种很有前途的加工方法。多元线性回归分析表明,油的抗氧化能力与甾醇、硬脂酸含量呈负相关,与亚油酸、花生酸、多不饱和脂肪酸含量呈正相关。这些信息对提高文冠果的营养价值和工业化生产具有重要意义。
论文简介:
文冠果是中国北方一种独特的木本油料灌木,被称为“北方油茶”,具有良好的生物学特性,如耐旱、耐温、耐瘠化、耐温和盐碱条件。在中医中,文冠果被用于治疗心脏病、血管疾病、遗尿、腹泻、脱发、皮肤病、智力迟钝、阿尔茨海默病等疾病。文冠果仁油已越来越多地应用于中国政府支持的植物油脂生产,以及化妆品、健康饮食和食品工业。
论文研究了四种不同提取工艺对文冠果仁油理化性质、营养成分和抗氧化能力的影响。文冠果仁油是一种很好的UFAs和营养物质来源。油脂提取方法不改变脂肪酸的组成,但改变了脂肪酸的含量。神经酸是油中含有的一种特殊脂肪酸,样品中其含量为2.73-3.09%。文冠果仁油是为数不多的能提供NA的食用油之一。HE的总生育酚和甾醇含量最高,分别为530.42 mg/kg和2105.06 mg/kg。SFE对DPPH自由基的清除率最高。多元线性回归分析表明,油的抗氧化能力主要与C20:0、PUFAs和甾醇有关,油的OSI主要与C18:0、C18:2(n-6)和甾醇有关。这些信息表明,文冠果营养成分丰富,具有较强的抗氧化能力,是一种潜在的食用油资源。为了使文冠果仁油能够大规模利用并实现工业化生产,还需要对其颜色、气味、多酚含量等指标进行进一步的评价。选择高甾醇和C18:2(n-6)含量的加工方法是提高文冠果仁油抗氧化能力的重要途径。
武汉轻工大学食品学院硕士研究生郑雨凌为该论文第一作者,武汉轻工大学食品学院高盼博士为该论文通讯作者。
作者简介:
高盼:武汉轻工大学食品科学与工程学院专任教师,中国粮油学会油脂分会理事,《中国油脂》青年编委。主要从事油脂及植物蛋白方向的研究,具有多年的核桃相关研究经验;获得国家自然科学基金青年基金项目 1 项,参与省部级科研项目 1 项,开放课题3 项;发表论文 30 余篇,其中 SCI论文14 篇;授权专利 1项;主编书籍 1 部;参与标准制修订 8项;主持横向项目 2 项。
郑雨凌:武汉轻工大学食品学院2020级学术型硕士研究生,专业为食品科学与工程,目前以第一作者在《molecules》期刊发表论文1篇。
论文原文: