Aptamer-modulated Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe) nanozymatic activity for the colorimetric detection of deoxynivalenol in grains
适配体调节Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe)纳米酶活性的比色法检测谷物中脱氧雪腐镰刀菌烯醇
Abstract
In this study, Pt/Au nanoparticles functionalized metal–organic frameworks (Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe)) nanocomposite was employed as a nanozyme and a colorimetric aptasensor based on aptamer-modulated nanozymatic activity was developed for deoxynivalenol (DON) detection. The catalytic activity of Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe) was initially inhibited by aptamers due to the blocking of surface-active sites. However, the presence of DON detached the aptamer from Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe) surface, restoring the enzyme-mimicking activity of the nanocomposites and producing a measurable colorimetric signal for DON quantitation. The nanozyme showed stable catalytic activities with a relative standard deviation within 3 % for storage at 4 °C for 21 days. Meanwhile, the developed aptasensor demonstrated a good linear range of 50–5000 ng/mL with a limit of detection of 44.14 ng/mL. The recovery rates for detecting DON in positive wheat and maize flour samples were 98.59 %–106.27 %. The developed method is cost-effective and easy to fabricate, providing a powerful tool for DON detection in food.
中文摘要:
在这项研究中,铂/金纳米颗粒功能化金属有机框架(Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe))纳米复合材料作为纳米酶,并开发了一种适配体调制纳米酶活性的比色适配传感器,用于脱氧雪腐镰刀菌烯醇(DON)检测。经适配体修饰后,表面活性位点被阻断,铂/金/MIL-100(Fe)的催化活性受到适配体的抑制。然而,DON与适配体结合后,从Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe)表面脱离,恢复了纳米复合材料的酶模拟活性,并产生了用于DON定量的可测量的比色信号。纳米酶显示出稳定,相对标准偏差在3%以内,4℃保存21天。同时,所开发的检测器在50-5000 纳克/毫升的范围内具有良好的线性,检测限为44.14纳克/毫升。在阳性小麦和玉米粉样品中检测DON的回收率为98.59 %-106.27 %。所开发的方法成本低廉,易于制造,为食品中DON的检测提供了有力的工具。
论文简介:
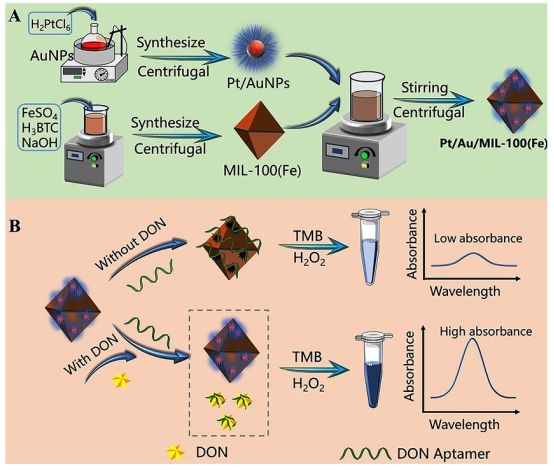
纳米酶是一类具有纳米材料特性和催化活性的酶模拟物,与天然酶相比,具有成本低、稳定性高和催化效率高等优点。本研究通过将Pt/Au纳米颗粒与MIL-100(Fe)结合,制备了具有过氧化物酶模拟活性的纳米酶,并利用适配体(Aptamer)调节其催化活性。
在本研究中,Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe)纳米酶的制备是通过将Pt/Au纳米颗粒均匀分散在MIL-100(Fe)表面实现的。该生物传感器的工作原理基于Aptamer对Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe)纳米酶活性的调节。在没有DON的情况下,Aptamer吸附在纳米酶表面,阻断了活性位点,抑制了其催化活性。当DON存在时,Aptamer与DON特异性结合并从纳米酶表面脱离,恢复了纳米酶的催化活性,从而催化TMB/HO₂体系产生蓝色产物。通过测量溶液在650 nm处的吸光度变化,可以实现对DON的定量检测。该纳米酶在4℃储存21天,显示出优异的长期稳定性。该比色法生物传感器在50-5000 ng/mL范围内对DON表现出良好的线性关系,检测限低至44.14 ng/mL。通过在大米、小麦面粉和玉米面粉中添加不同浓度的DON进行回收率测试,结果表明,该生物传感器的回收率在97.32%-110.95%之间,相对标准偏差小于8%,与商业ELISA试剂盒相当。这表明该生物传感器在实际应用中具有较高的准确性和可靠性。
本研究开发的Pt/Au/MIL-100(Fe)纳米酶比色法生物传感器不仅为DON的检测提供了一种快速、灵敏的方法,还为纳米酶在食品安全检测中的应用提供了新的思路。未来,该技术有望进一步推广至其他真菌毒素的检测,为保障食品安全和公共健康做出贡献。
该研究成果于2025年2月发表于国际学术期刊“Food Chemistry”。食品学院戴煌博士、硕士研究生余俊兰为论文第一作者,皮付伟教授为通讯作者。该研究得到了国家重点研发计划(2022YFF1102500)的资助。
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143378
